Granica for Geospatial Intelligence Companies
Learn how Granica helps.
Digital maps and location services have become a nearly ubiquitous part of modern life with a wide range of applications and uses for both consumers and enterprises alike, from navigation and geomarketing to supply chain management and infrastructure planning. The geospatial intelligence companies behind these services are investing in AI and machine learning to improve the accuracy and functionality of their services. Common use cases include:
- Creating immersive 3D maps
- Identifying and labeling map features
- Predicting traffic patterns
- Optimizing routing.
The challenge
To build their services, geospatial intelligence companies capture, aggregate, and analyze data from a wide range of sensors and sources such as high resolution aerial cameras, LiDAR, RADAR, IoT, and mobile devices. The volume of data is tremendous and can easily grow to tens of petabytes, costing millions of dollars annually even when stored in "low-cost" cloud object stores. Data at this scale also puts a strain on the entire AI pipeline from both a cost and time perspective.
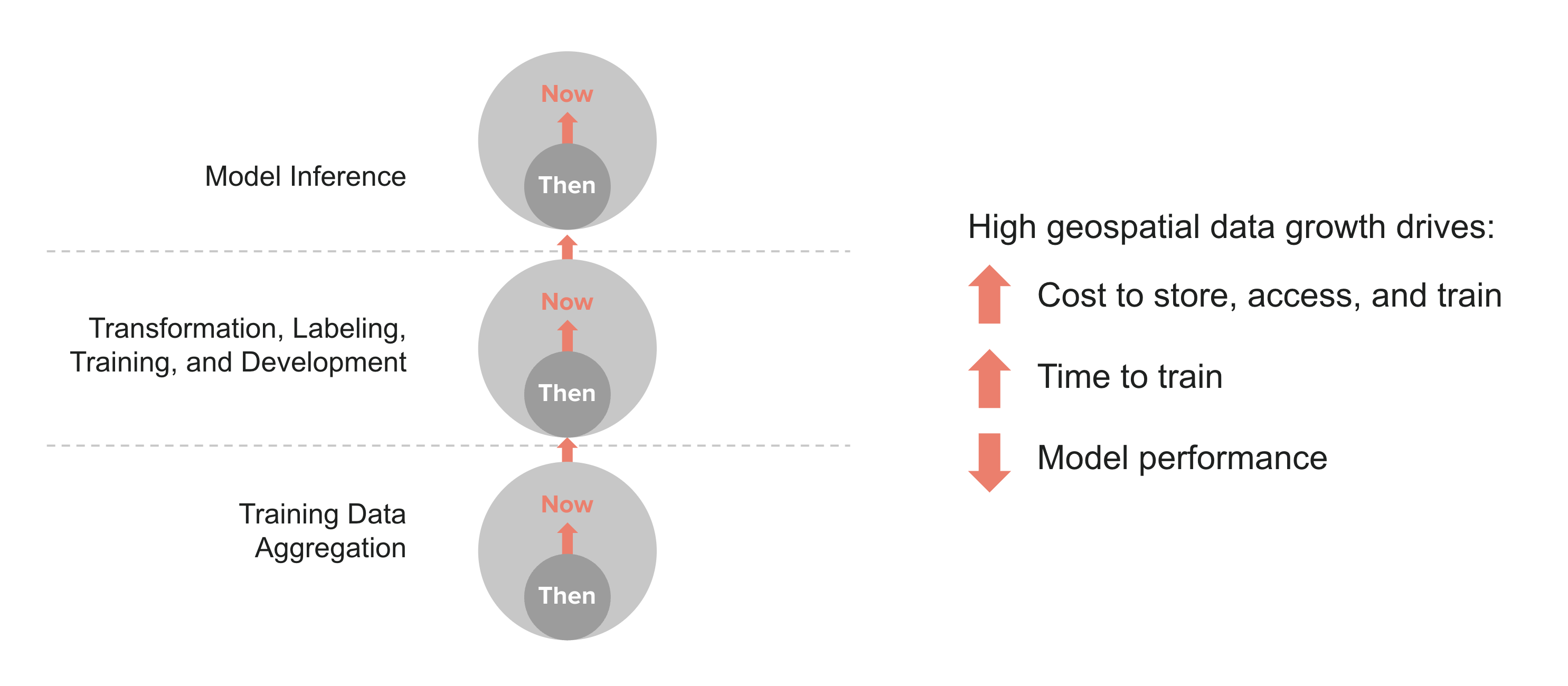
For geospatial intelligence companies, all data is hot data which must be quickly ingested, analyzed, and acted upon in order to generate value. As a result, companies typically build their AI data infrastructure around leading cloud object storage offerings such as Amazon S3 Standard and GCS Standard rather than archival tiers such as Amazon S3 Glacier and GCS Archive. Archival tiers are not only slow and asynchronous, they also come with heavy read access and data transfer costs. Those same access costs also preclude usage of faster object storage tiers such as Amazon S3 Infrequent Access (IA) and GCS Nearline. While S3/GCS Standard tiers are thus the most cost-effective given the processing needs of AI, the volume of data means that storage-related costs are still large and growing rapidly.
Making matters worse, geospatial source data typically contains significant redundant and low-value content. Such content works to reduce the "signal to noise" in the data, and also increases the resource cost and time to move it through the end-to-end pipeline.

Taken together these data costs are consuming ever more of the AI innovation budget and crowding out investment in compute, tooling, and people. For AI product owners and AI/ML engineers the result is the same - higher costs and less effective outcomes. Simply put, the ROI on AI for geospatial intelligence companies is lower than it needs to be.
How Granica helps
Granica is a new layer in the AI stack which increases the efficiency and utility of your AI-related data and thus your downstream AI pipeline stages, enabling you to free up significant money, resources, and time which you can reinvest to improve AI performance and outcomes. We achieve these efficiency gains today via our product Granica Crunch, with additional services coming soon.
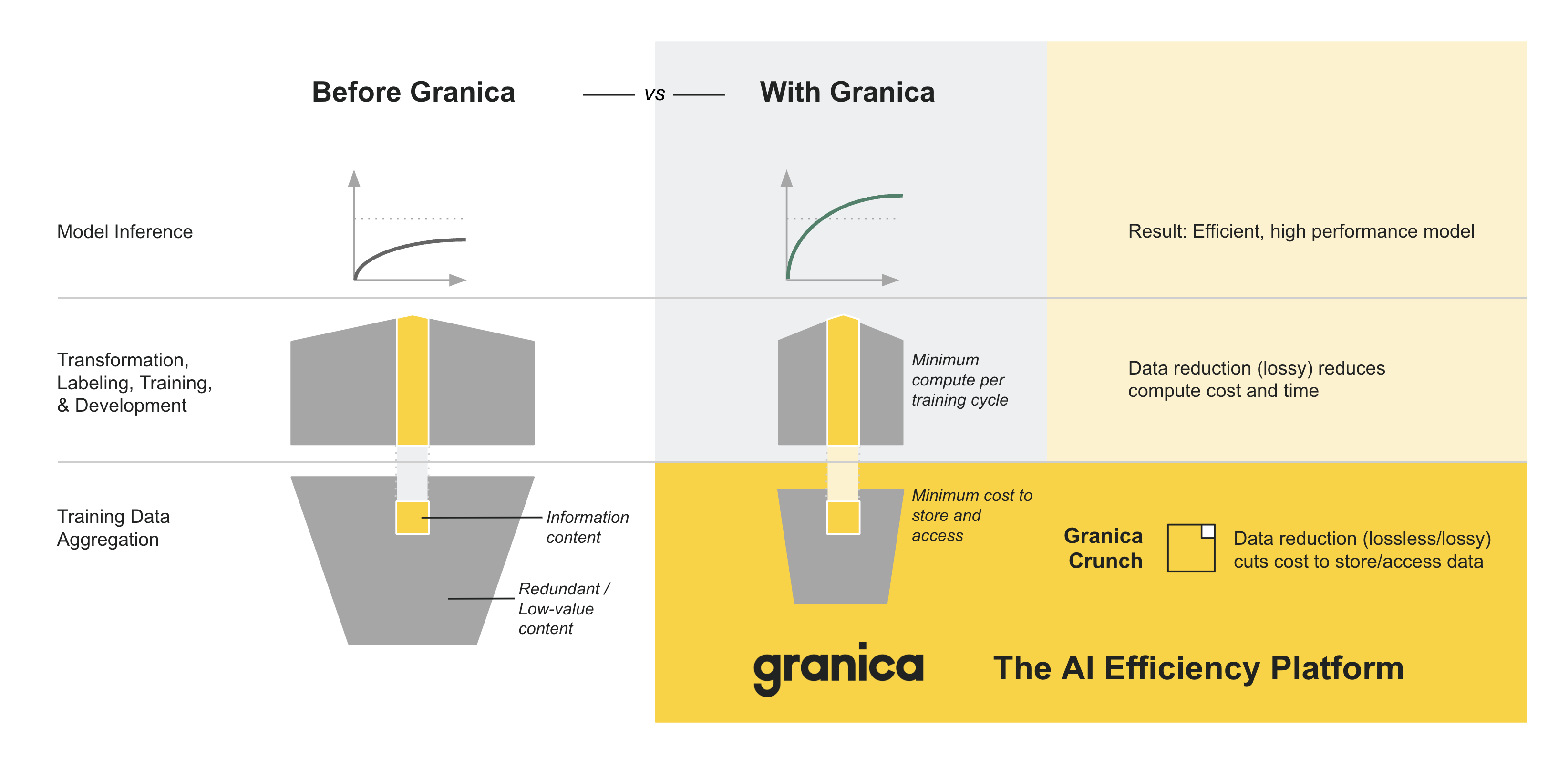
Granica Crunch: data reduction for geospatial data
Granica Crunch reduces the storage cost associated with AI data without archival and/or deletion. Its advanced, patented machine learning-powered data reduction algorithms are specifically optimized for the image / LiDAR / tabular data prevalent in the geospatial intelligence industry.
How Crunch helps AI/ML Engineers
- Optimizes S3/GCS object storage costs, so you can allocate more resources to what matters most: data quality and model performance
- Supports a wide range of data types unique to the development of location and mapping systems, but we are open to further customization for your particular needs. Crunch also supports pre-compressed and archived formats
- Elastically scales up and down to support your dynamic workloads
- Is easily consumed as an API by your applications directly working with data in S3/GCS
How Crunch helps AI Product Owners and FP&A
- No upfont capital outlay eliminates the need to find or reallocate budget and thus accelerates your time to value. Crunch doesn’t cost budget, it frees up budget
- Ongoing, predictable savings enable you to accurately forecast and plan where and how to apply them
Data reduction eliminates redundant data
Crunch runs transparently in the background to losslessly reduce storage and access costs. The Crunch data reduction rate (DRR) varies by file type, and total savings also varies based on access patterns. The following table illustrates the typical DRR we have seen in production customer environments for geospatial data:
| Type | e.g. files | DRR |
|---|---|---|
| Images | .png, .tiff | >50% |
| LiDAR | .las, rosbag, etc. | 25-50% |
| Tables | .parquet | >50% |
DRR also varies based on the customer-specific data contained inside each file type. Estimate your savings to quickly evaluate the DRR for your specific data.